How does bronchitis check, what should notice?
summary
Bronchitis is a common respiratory disease, which is caused by biological, physical, chemical stimulation or allergic factors. Now let's talk about how to check for bronchitis.
How does bronchitis check, what should notice?
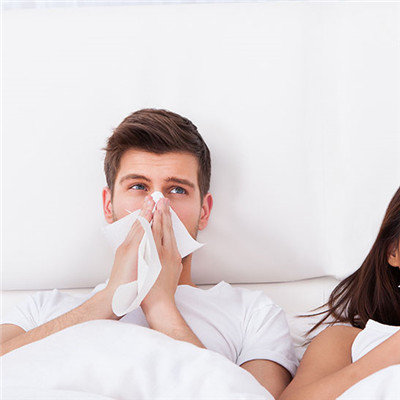
First: acute bronchitis is often manifested as upper respiratory tract infection symptoms in the early stage of onset, patients usually have nasal congestion, runny nose, sore throat and hoarseness and other clinical manifestations. The general symptoms are mild, but there may be low fever, chills, fatigue, conscious throat itching, irritating cough and retrosternal pain. In the early stage, the amount of sputum was not much, but the sputum was not easy to cough up. 2-3 days later, the sputum could change from mucinous to mucopurulent. Cold, inhaling cold air or irritant gas can aggravate or induce cough. The cough is often obvious in the morning or at night. Cough can also be paroxysmal, sometimes persistent cough. Severe cough is often accompanied by nausea, vomiting and chest, abdominal muscle pain. If accompanied by bronchospasm, there may be wheezing and shortness of breath.
Second: chronic bronchitis refers to patients with chronic cough and expectoration for more than three months every year for two consecutive years, excluding other causes of chronic cough. It is not necessarily accompanied by persistent airflow limitation. (1) long term, repeated and gradually aggravating cough is the prominent manifestation of the disease. Mild cases only occur in winter and spring, especially before and after getting up in the morning. Cough is less in the daytime. In summer and autumn, cough is relieved or disappeared. Severe patients cough in all seasons, especially in winter and spring, day and night. (2) expectoration of sputum is usually white mucous and foam, which is more frequent in the morning. After infection or cold, the symptoms quickly worsened, the amount of sputum increased, viscosity increased, or yellow purulent sputum or accompanied by wheezing. Occasionally, the sputum is bloody due to severe cough. (3) wheezing when complicated with respiratory tract infection, due to congestion and edema of bronchiolar mucosa, obstruction of sputum and stenosis of bronchial lumen, asthma (wheezing) symptoms may occur. Wheezing occurred in the throat during breathing and wheezing occurred in the lung during auscultation.
Third: diet should be light, avoid spicy meat. Should quit smoking and drink more tea, because smoking will cause respiratory secretions increase, reflex bronchospasm, sputum difficult, conducive to the growth and reproduction of viruses and bacteria, make chronic bronchitis further worse. Tea contains theophylline, can excite sympathetic nerve, make bronchiectasis and reduce cough and asthma symptoms.
matters needing attention
In the acute stage, according to the doctor's advice, choose effective antimicrobial treatment. Commonly used drugs: compound sulfamethoxazole, strong toxin, erythromycin, etc. When the treatment is invalid, the drugs that the patient has not used or seldom used, such as medicin and spiramycin, can be selected. After the control of acute infection, antibacterial drugs should be stopped in time to avoid side effects caused by long-term application.