Neisseria gonorrhoeae infection symptoms?
summary
Neisseria gonorrhoeae is commonly known as Neisseria gonorrhoeae, which is a strict human parasite. It often exists in the white blood cells of purulent secretions of acute urethritis and vaginitis. Its morphological staining is similar to meningococci. Neisseria gonorrhoeae infection can cause pyogenic infection of genitourinary system, is one of the common sexually transmitted diseases, commonly known as gonorrhea. Neisseria gonorrhoeae infection symptoms? Let's talk about it
Neisseria gonorrhoeae infection symptoms?
Male gonorrhea (1) the incubation period of male acute gonorrhea is generally 2-10 days, with an average of 3-5 days. The urethra began to burn, itch, redness and eversion. Burning pain during micturition, accompanied by frequent micturition, and a small amount of mucinous secretion at urethral orifice. 3-4 days later, most of the urethra mucosa epithelium had focal necrosis, produced a large number of purulent secretions, and had sharp pain during urination, glans and prepuce redness and swelling. Drenching wire or blood can be seen in the urethra, and pus scab can be formed at the urethral orifice when getting up in the morning. With different degrees of systemic symptoms. ② Male chronic gonorrhea generally has no obvious symptoms, when the body resistance is reduced, such as excessive fatigue, drinking, sexual intercourse, can appear urethritis symptoms.

Female gonorrhea (1) the symptoms of female acute gonorrhea infection are mild or asymptomatic. After the incubation period of 3-5 days, urethritis, cervicitis, paraurethral adenitis, vestibular adenitis and proctitis appear successively, among which cervicitis is the most common. 70% of female gonorrhea patients had urethral infection. Gonococcal cervicitis is common and often occurs at the same time as urethritis. ② Chronic gonorrhea and acute gonorrhea in women can be turned into chronic gonorrhea without adequate treatment. The symptoms were abdominal distension, backache and leucorrhea. ③ Pregnancy complicated with gonorrhea has no clinical symptoms. When pregnant women with gonorrhea give birth, they can infect the fetus through the birth canal, especially when the fetal position is breech presentation, which can cause premature rupture of membranes, amniotic infection, premature delivery, postpartum sepsis and endometritis. ④ Gonococcal vulvovaginitis in young girls, with redness and swelling of vulva, perineum and perianal, and more purulent vaginal secretions, can cause urination pain, local irritation and ulceration.

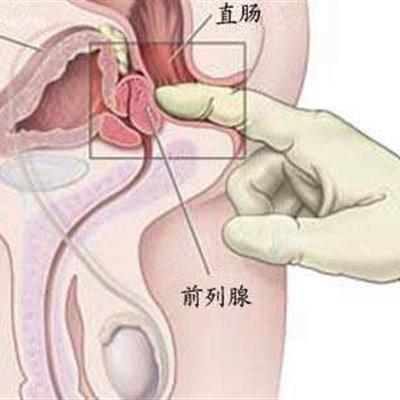
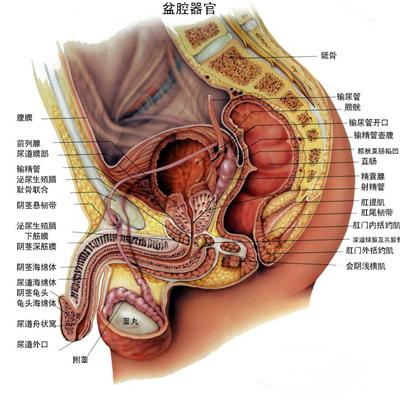
Male gonorrhea complications: 1. Prostatitis and seminal vesiculitis. If the seminal vesicle is involved, the semen may be mixed with blood. When complicated with prostatitis, perineum pain, rectal digital examination prostate enlargement, pain, seminal vesicle gland enlargement. ② Epididymitis and bulbar urethritis have pain, swelling and tenderness in epididymis. When complicated with bulbar urethritis, the perineum may touch the enlarged glands, and the patient may feel uncomfortable or dull pain. When complicated with acute epididymitis, scrotal swelling, pain, epididymis swelling, spermatic cord thickening. ③ The stimulation of purulent secretion of gonococcal balanitis can cause balanitis and prepuce inflammation. * glands, urethra, retention cysts, lymphadenitis, lymphadenitis and anterior urethral recess and glands of prepuce glands can be invaded, called adenourethritis. * if these glands are blocked, they can form retention cysts, which can form cysts around the urethra after ruptured cysts. Paraurethral gland or periurethral inflammation can extend to the corpus cavernosum, often complicated with lymphangitis, unilateral or bilateral inguinal lymphadenitis. The prepuce glands on both sides of the frenulum of the penis can also be involved to form an abscess.

matters needing attention
(1) First of all, the diagnosis should be established as soon as possible after the illness, and the treatment should not be arbitrary before the diagnosis. Second, the diagnosis should be treated immediately( 2) To identify the clinical types and judge whether there are complications. It is very important to make clear the clinical classification for correctly guiding the treatment( 3) It is helpful to guide the treatment correctly to know whether there is drug resistance and whether it is resistant to penicillin and tetracycline( 4) If chlamydia or mycoplasma infection is combined, a combined drug treatment plan should be formulated.