Symptoms of zygomatic fracture
summary
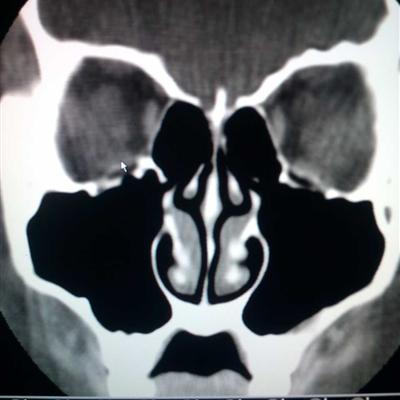
Zygoma and zygomatic arch are prominent parts of the face, which are vulnerable to impact and fracture. Zygomatic bone is associated with maxilla, frontal bone, sphenoid bone and temporal bone, among which the joint surface with maxilla is the largest. The temporal process of zygoma and zygomatic process of temporal bone are connected to form zygomatic arch, which is thinner and narrower and more prone to fracture. Symptoms of zygomatic fracture? Let's talk about it
Symptoms of zygomatic fracture
After zygomatic bone and zygomatic arch fracture, the displacement direction of the fracture block mainly depends on the direction of the external force, and most of them are invaginated. In the early stage after injury, zygomatic facial depression can be seen. Subsequently, due to local swelling, depression deformity is not obvious, which is easy to be mistaken for simple soft tissue injury. After a few days, the swelling subsided and local collapse appeared.
After zygomatic fracture displacement, diplopia can be found due to eye displacement, abducens muscle bleeding and local edema, as well as tear of the anterior oblique muscle embedded in the fracture line, limiting eye movement and other reasons.
Because of the displacement of the fracture block, the temporalis and masseter muscles are compressed, and the movement of the coracoid process is hindered, resulting in pain and limitation of mouth opening. When there is a closed fracture of the zygomatic orbital wall, there may be hemorrhagic ecchymosis under the periorbital skin, eyelid and conjunctiva.
matters needing attention
The treatment of zygomatic bone and zygomatic arch fracture is mainly surgical reduction. After zygomatic bone and zygomatic arch fracture, all patients with dysfunction should be treated with reduction. If there is no displacement or no obvious displacement and no dysfunction, special treatment is not necessary. After reduction of zygomatic bone and zygomatic arch fracture, in order to prevent the fracture segment from shifting again, mouth opening movement should be appropriately limited to avoid collision, and healthy lateral position should be used during sleep.