How long does the paralyzed old man live?
summary
How long does the old man live after paralysis? When people get old, there will be various diseases in their bodies. Some diseases will lead to paralysis of the elderly, which has a great impact on their later life. How long will the elderly live after paralysis? Now let me introduce it to you.
How long does the paralyzed old man live?
In fact, there is no fixed date for how long the paralyzed elderly can live. This is because, in the process of nursing the paralyzed elderly, whether the nursing method is obtained and the elderly's own physique and other factors will have an impact on their life. After the old man was paralyzed, he just had problems walking. If he had a good attitude and his family took good care of him, his health would not be much worse than that of the normal old man. As for how many years he could live, it's hard to say.
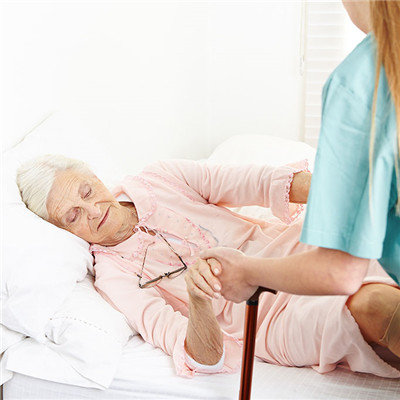

According to personal habits, reasonable allocation of diet, food diversification, eat more cellulose containing vegetables, fruits. After brushing teeth in the morning, drink 300ml cold boiled water or warm honey water to moisten intestines and promote peristalsis. In addition, strengthen the functional exercise of abdominal wall muscle and levator ani muscle. At the other end of the bed, fasten a strong cloth belt or belt, firmly grasp the cloth belt with both hands, pull up the upper body with the help of external force, then put it down, and continuously exercise according to your ability. Persisting in it will help defecate, prevent bedsore and increase vital capacity.

Paraplegic patients are prone to bedsore due to long-term compression and poor blood circulation. Therefore, it is necessary to prevent and control as soon as possible, keep the sheets flat and clean, add an air ring at the bone protrusion, turn over more, change the body position every 2 hours, and massage with 50% ethanol. It can promote the functional recovery of paralyzed limbs by passive activities, massage, acupuncture and physiotherapy. Prevent muscle atrophy, joint stiffness, bone decalcification, etc. Pay attention to keep the limbs in the functional position to prevent deformity. After 3 months of traumatic paraplegia, the patient could sit up and begin crutches.
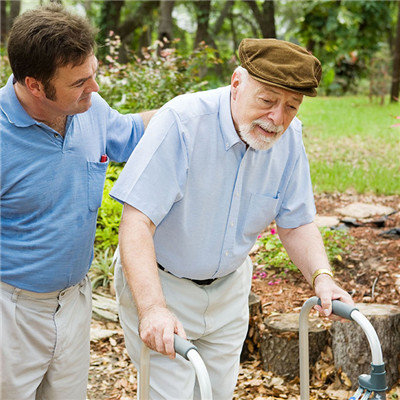

matters needing attention
Prevention of pulmonary complications: quit smoking absolutely, turn over regularly, pat on the back, encourage patients to take deep breath and expectorate effectively, atomize inhalation when necessary, and keep the respiratory tract unobstructed. The patients with high paraplegia were treated with tracheotomy and antibiotics. Psychological nursing: patiently listen to patients, understand the degree of their psychological barriers, respect, care and care for patients.