How does acute radiation thyroiditis not treat?
summary
Acute radio thyroiditis (Art) refers to the inflammation of the thyroid gland that occurs within two weeks after acute radiation. The thyroid gland is usually less sensitive to the direct effects of radiation, but the proliferative thyroid gland is more sensitive to radiation. Therefore, the thyroid gland of minors and patients with hyperthyroidism is more sensitive to radiation, which is easy to cause thyroiditis. Let's share my experience with you.
How does acute radiation thyroiditis not treat?
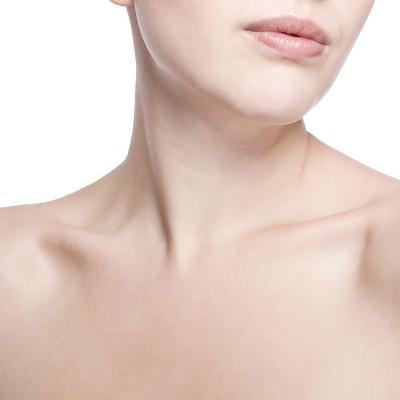
Radiation thyroiditis has a history of radiation therapy, often occurs within 1-2 weeks after 131I or 125I treatment of hyperthyroidism and thyroid cancer. Acute symptoms are generally mild, manifested as a sudden onset of local thyroid pain, tenderness, neck swelling, and sometimes transient hyperthyroidism.

For mild cases, no special treatment is needed, and most of the symptoms can disappear spontaneously after 3-4 weeks. When the pain is obvious, non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can be used. For severe cases, corticosteroids, such as prednisone, can be used for treatment.

About 1-5% of patients with hyperthyroidism developed acute radiation thyroiditis during 131I treatment; The incidence of acute radiation thyroiditis can reach 2% - 30% due to the different amount of residual thyroid tissue after radionuclide iodine therapy.

matters needing attention
In some patients with hyperthyroidism treated with 131I, the symptoms of hyperthyroidism will worsen, even thyroid crisis. This is mainly due to the destruction of thyroid follicles, a large number of thyroid hormones rapidly released into the blood.