Sacral seminal chordoma symptoms?
summary
The common benign tumors of the sacrum include osteoblastoma, giant cell tumor of bone and aneurysmal bone cyst, and the common malignant tumors of the sacrum include chordoma and chondrosarcoma. Metastatic carcinoma of the sacrum is rare. Comprehensive treatment and surgical treatment are the first choice for most sacral tumors. Sacral seminal chordoma symptoms? Let's talk about it.
Sacral seminal chordoma symptoms?
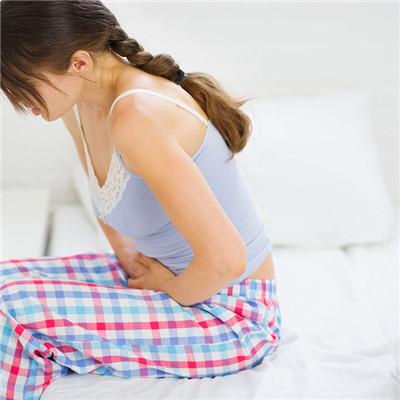
Pain is the earliest symptom, which is usually caused by tumor expansion, invasion or compression of adjacent important tissues or organs. Tumors located in the sacrococcygeal region often cause pain in the tail, and then local masses appear, and gradually grow up, from subcutaneous uplift, can also develop into the pelvic cavity, oppressing the bladder and rectum, causing urinary incontinence and constipation, The tumors located in the sphenoid occipital region can compress the optic nerve and other brain nerves, pituitary gland, brain stem, etc., and can cause intracranial hypertension in the later stage. The patients with spinal cord compression around the spinal canal can cause root pain, paraplegia, incontinence of urine and feces, etc
Chordoma is more common in middle-aged and elderly people aged 40-60 years, occasionally in children and young people. The tumors are mainly located at both ends of the spine, namely the skull base and sacral vertebrae. The former is 35%, the latter is 50%, and other vertebrae are 15%. It is rare to occur outside the longitudinal axis, such as transverse process of vertebrae, nasal sinus bone, etc, The vast majority of intraspinal chordomas usually experience symptoms for months to years before diagnosis
The clinical symptoms are determined by the location of the tumor: occipital and sphenoid tumors can produce headache, cranial nerve compression symptoms (optic nerve is the most common), pituitary dysfunction can occur if pituitary gland is damaged, protruding laterally or downward can form a mass in the nasopharynx, block the nasal cavity, appear purulent secretions, and headache often occurs when it occurs at the lower slope and craniocervical junction, Occipital or occipitocervical junction pain is a common symptom, which can be aggravated when head posture changes; If the tumor occurs in the thoracic vertebrae, it can invade the corresponding vertebral structure, protrude into the thoracic cavity through the intervertebral foramen, and destroy the intercostal nerve, which can cause segmental burning neuralgia, and even pulmonary pleural irritation. If the tumor occurs in the sacrococcygeal region, the compression symptom of the sacrococcygeal region appears later, and the main symptom is sacrococcygeal pain. The typical symptom is chronic lumbocrural pain, which is aggravated continuously at night, The history can be as long as 0.5-1 year. When the tumor is large, the mass compresses the pelvic organs forward and compresses the sacral nerve root, causing incontinence, dysuria, numbness or pain of lower limbs and buttocks. The mass can produce mechanical obstruction, resulting in dysuria and constipation. If it occurs in other parts of the spinal canal, local pain is the common symptom
matters needing attention
The probability of chordoma metastasis is not high. Chordoma located in the sacrococcygeal region has more metastasis than that in the skull base and the spine above the sacrum. It usually occurs 10 years after the occurrence of the tumor. The local lymph nodes are often involved, and then the blood is transported to the lung, liver and peritoneum, The prognosis of chordoma is better than that of chordoma