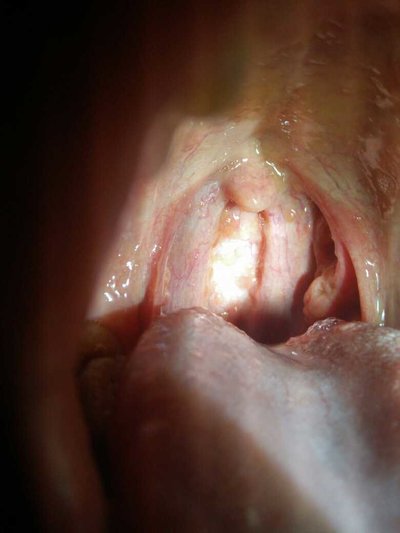
What symptom does scald infection have?
summary
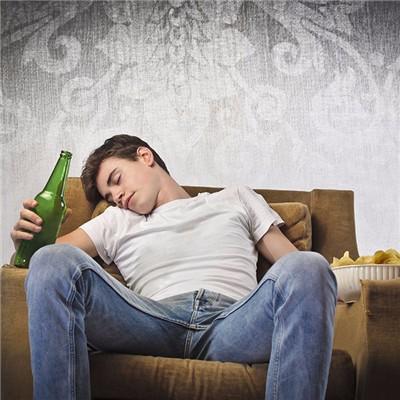
When we are scalded, we should take care of the wound carefully, because if we don't pay attention, the wound will be infected. The harm caused by scald infection is great, such as sepsis and bacteremia, and the possibility of renal failure. The treatment of complications caused by it is very difficult, so it is very important to clean the scalded part. What symptom does scald infection have? The following describes the symptoms of infection.
What symptom does scald infection have?
Sepsis: cells (or other microorganisms) invade the blood stream and propagate in the blood or organs and tissues. At the same time, they produce a large number of mycins and products, causing systemic clinical symptoms, accompanied by changes in hemodynamics and metabolism-- It's called sepsis. If septic shock occurs, the prognosis is poor. The diagnosis of sepsis is usually based on positive blood culture. The bacteria causing sepsis may come from burn wound, venous catheter infection, visceral infection, or enterogenous infection. Sepsis is the late manifestation of wound toxicosis.

Bacteremia: the transient appearance of living bacteria in the blood circulation is called bacteremia. It often occurs in the process of escharectomy or decrustation of scald wound, with mild clinical symptoms and no changes in hemodynamics and blood biochemistry.

Burn wound sepsis: Pseudomonas aeruginosa propagates in the normal tissue around the burn wound, invades lymphatic vessels and vascular walls or penetrates into blood vessels to form embolism. The release of a large number of endomycin into the blood circulation, the clinical symptoms of sepsis, blood culture is often negative, known as burn wound sepsis. There was perivasculitis or vasculitis in the tissue biopsy around the wound. The amount of bacteria in the tissue around the wound is generally greater than 105 / g tissue. However, this index is not an index for the diagnosis of wound sepsis. It should be judged by biopsy and systemic symptoms.

matters needing attention
1. Glucocorticoid. It can directly antagonize or neutralize the lipopolysaccharide and stabilize the complement of E. coli. 2. Diglycol disodium (DSCG). Application of cromogenol disodium can stabilize mast cells and neutrophils without releasing histamine, serotonin and slow hypersensitive substances, thus blocking the effects of these transmitters on the whole body. 3. Polymyxin B and its antibiotic. Literature data show that polymucin B can neutralize endomycin, and carbenicillin can also neutralize E. coli endomycin.