Symptoms of actinomycete infection?
summary
Actinomycosis is a chronic suppurative and granulomatous disease caused by actinomycetes of the genus actinomycetes. It is characterized by fistula formation and outflow of pus with sulfur yellow particles. Buccal ulcer of traditional Chinese medicine is similar to maxillofacial actinomycosis. Yizong Jinjian: surgical mental skill? Records: "buccal ulcer stomach heat accumulation, such as red millet at the beginning, purulent swelling disappear, easy to recover, purulent difficult to gather leakage due to.".
Symptoms of actinomycete infection?
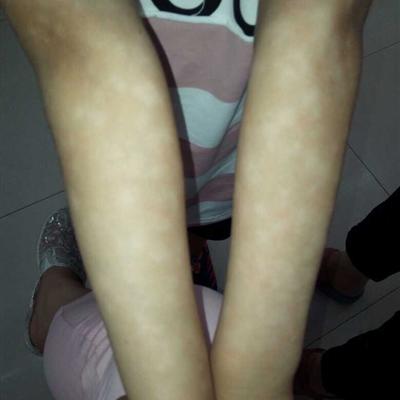
Actinomycosis of the face and neck is the most common disease, which can be parasitized in the mouth first. The pathogen can invade from caries or periodontal abscess, tonsil lesions, etc. It mainly occurs at the junction of the face and neck. The skin color is dark red or brown, and then it forms abscess. The local plate is hard. The abscess breaks through into many pus drainage sinuses, and the "sulfur particles" are common in the pus drainage. The lesions can extend to the skull, neck and neck When the masticatory muscles are involved in the shoulder and chest, the teeth can be closed tightly, and the lower periostitis and osteomyelitis can be caused later.

Abdominal actinomycosis is caused by oral ingestion and invasion of intestinal mucosa. It can also be directly affected by chest lesions. It often occurs in ileocecal region, such as acute, subacute or chronic appendicitis, local mass plate hardness, and then through the abdominal wall to form a fistula. Sulfur particles can be seen in the pus, accompanied by fever, night sweats, fatigue, emaciation and other systemic symptoms, It can also affect other abdominal organs, such as stomach, liver, kidney, etc., or affect vertebrae, ovary, bladder, chest or hematogenous dissemination, and invade the central nervous system.

The pathogenic bacteria of chest actinomycosis enter the lung through respiratory tract and cause disease. It can also be directly affected by the adjacent actinomycosis. It often invades the hilar or the bottom of the lung and presents acute or chronic infection, such as irregular fever, chest pain, cough, expectoration with blood, night sweats, emaciation, etc, X-ray showed consolidation of pulmonary lobes, in which there may be transparent areas, pleural adhesion and pleural effusion, and pericarditis.

matters needing attention
Pay attention to oral hygiene, early treatment of teeth, periodontal and tonsillar diseases. Respiratory tract, digestive tract inflammation and ulcer focus should be treated as early as possible to avoid the formation of chronic infection focus.