Symptoms of ozone poisoning?
summary
Ozone is the allotrope of oxygen, which is composed of three oxygen atoms. It's a light blue gas with a pungent odor. If the concentration is higher than 100ppm, it will cause respiratory disorders and headache. Nitrogen dioxide emitted from automobiles, chemical factories and power plants, after absorbing sunlight, is converted into nitric oxide and active oxygen atoms, which then react with oxygen to form ozone. These stay in the troposphere of ozone will make people feel difficult to breathe, lung function and lung tissue damage. In addition, ozone will interact with hydrocarbons emitted from cars to generate photochemical fog, which stimulates our respiratory system.
Symptoms of ozone poisoning?
Low concentration of ozone can disinfect. In general, the concentration of ozone in forest areas can reach 0.1ppm, but the excessive ozone is an invisible killer! In summer, due to the influence of industrial and automobile exhaust, especially around big cities and agricultural and forestry areas, surface ozone will form and accumulate. Ozone on the surface of the human body, especially on the eyes, respiratory tract and other erosion and damage. Surface ozone is also harmful to crops or forests.
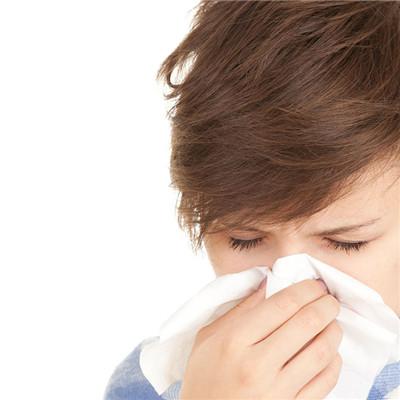
Ozone can stimulate mucous membrane, which is toxic to human body. It is not safe to breathe in the air containing 0.1ppm ozone for a long time. It strongly stimulates the respiratory tract, causing sore throat, chest tightness, cough, bronchitis and emphysema; Ozone can cause neurotoxicity, dizziness, headache, vision loss, memory loss, shortness of breath, fatigue and nosebleed; ▲。
Ozone can destroy vitamin E in human skin, causing wrinkle and black spots; The ozone can also destroy the immune function of human body, induce lymphocyte chromosomal lesions, accelerate aging, and cause pregnant women to have abnormal babies; Therefore, people must pay more attention to the harm caused by ozone and organic waste gas.
matters needing attention
Diseases caused by inhaling excessive ozone. Acute poisoning can produce eye, respiratory tract irritation symptoms, severe cases can occur chemical bronchitis, pneumonia, and toxic pulmonary edema. Short term inhalation of low concentration ozone can cause dry oropharynx, tightness behind sternum, cough and expectoration. Long term inhalation of low concentration ozone, drowsiness, fatigue, decreased working ability, decreased vision, abnormal taste, etc., can also occur bronchitis, even emphysema or pulmonary sclerosis. In addition to disengagement, necessary symptomatic treatment should be used.