How is mammary gland radiate swelling to return a responsibility?
summary
Radiotherapy for breast cancer is an important treatment for breast cancer, but everything has two sides. Radiotherapy may also bring some adverse reactions, which is closely related to the specific location and dose of radiation. In general, compared with other tumors (such as head and neck tumor, lung cancer, esophageal cancer), the adverse reactions caused by radiotherapy in breast cancer patients are relatively mild. How is mammary gland radiate swelling to return a responsibility? Let's talk about it.
How is mammary gland radiate swelling to return a responsibility?
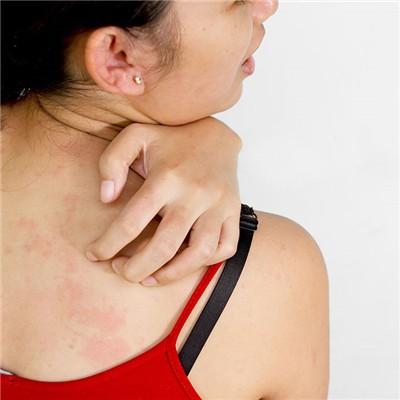
Local breast reaction in patients with breast conserving surgery, in postoperative radiotherapy, only the breast will be irradiated, and the adverse reactions caused by radiotherapy are the least. In the whole process of radiotherapy, the most important reaction is skin reaction, which is manifested as skin fever, skin color darkening and reddening, dry small pieces peeling, hair follicles blackening, breast tissue swelling, accompanied by pain. In terms of severity, these reactions are mild for most patients and will not affect their daily activities and rest. However, due to improper nursing or individual differences, a small number of patients may have relatively obvious reactions. At the end of radiotherapy, wet peeling of breast skin may occur, which is manifested as small pieces of skin falling off and damaged, local superficial ulcer, accompanied by exudative pain, especially around the nipple. There are a very small number of patients may appear throughout the breast obvious red, swelling, pain, and even need to take oral painkillers. After radiotherapy, the incidence of long-term breast reaction is very low, only a small number of patients may have the late reaction of local breast hardening and fibrosis, but the overall shape of the breast changes little.
Systemic reactions some patients may have systemic reactions, such as mild nausea, general fatigue, drowsiness, abnormal blood routine, etc. abnormal blood routine mainly includes leukopenia, lymphopenia, anemia, etc., which usually does not affect the continuation of radiotherapy.
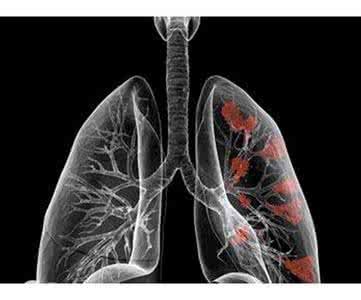
Because the lung is behind the mammary gland, the ipsilateral lung will be exposed to some radiation during radiotherapy. Generally, this dose level of radiation is completely tolerable to the lung, so almost few patients will have cough, shortness of breath and other respiratory symptoms due to breast radiotherapy. However, very few patients may have cough, shortness of breath, etc. after radiotherapy, and sometimes they may need treatment. When this happens, they should see a doctor in time and follow the doctor's advice. It should be noted that in the follow-up process after radiotherapy, chest CT or chest X-ray examination is likely to have similar description of "lung fiber streak shadow, changes after radiotherapy" in the examination report. Patients do not need to worry. This is a normal change after treatment, which will not cause clinical symptoms and discomfort, and has no effect on respiratory function.
matters needing attention
In some patients, the scope of postoperative radiotherapy will include the neck, and transient pharyngeal pain may occur during radiotherapy, especially when swallowing. This is because in the neck radiotherapy, the irradiation range is close to the pharynx, and some scattered dose irradiates the mucosa of these parts, causing mucosal erosion and inflammation, leading to pain. This kind of symptom usually begins to appear around the third week of radiotherapy, and will be self-healing after 1-2 weeks. There will be no impact on the long term.