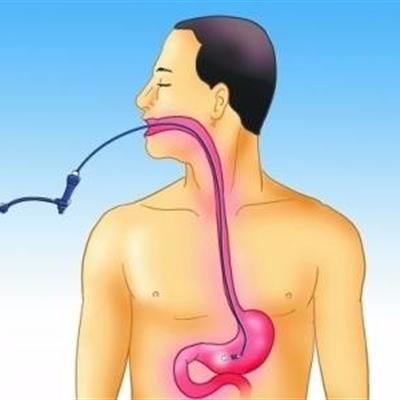
Precautions for painless gastroscopy
summary
Chronic gastritis often has a certain degree of atrophy (loss of mucosal function) and metaplasia, often involving the cardia, accompanied by loss of G cells and decreased gastrin secretion, can also involve the gastric body, accompanied by the loss of acid secreting glands, resulting in the reduction of gastric acid, pepsin and endogenous factors. So we must do a good job of the disease related work, then do painless gastroscopy precautions.
Precautions for painless gastroscopy
First: avoid eating all kinds of irritating food, such as strong liquor, espresso, raw garlic mustard and other food that damage the gastric mucosa, and avoid eating hard, too sour, too spicy, too cold, too hot and too rough food. Can choose easy to digest food, and pay attention to use less fried, fried and other cooking methods. The food should be light, soft and rotten.
Second: increase nutrition, pay attention to choose high nutritional value of protein food and vitamin rich soft food, such as milk, tofu, carrots and some fermented food, food to chew slowly.

Third: diet should be regular, regular and quantitative, do not overeat, develop good eating habits, reduce the burden on the stomach. If the amount of three meals is small, the meal can be added regularly between meals. Pay attention to food collocation, it's better to have dry and thin food, protein food and a small amount of staple food.

matters needing attention
I would also like to emphasize that anti parietal cell antibodies can be found in the blood and gastric juice of some patients with atrophic gastritis, and there is diffuse lymphocyte infiltration in the gastric mucosa. It is believed that the autoimmune reaction may be related to the occurrence of atrophic gastritis. The pathological changes of superficial gastritis were congestion, edema, exudation, erosion and bleeding of gastric mucosa; atrophic gastritis was flat or disappeared of mucosal folds; hypertrophic gastritis was thickening of mucosa and hyperplasia of epithelial cells. The main clinical manifestations are dyspepsia, epigastric pain after eating, anemia and upper gastrointestinal bleeding.