What branch is kidney cyst
summary
Renal cyst is a disease of renal internal medicine, which is common in young people aged 30-40. Incidence rate is high. According to the statistics of authoritative institutions, the incidence of renal cyst is 10%, which increases with age. The incidence of 40 years old is lower than that of 80 years old. Let's talk about what department is renal cyst.
What branch is kidney cyst
First of all: renal lesions belong to urological diseases, renal cyst is a benign lesion, there is no effect when taking medicine, if it is not too large, do not need treatment, regular review of color Doppler ultrasound can be, if the cyst diameter is more than 6 cm, can consider interventional treatment, small trauma, low cost, fast body recovery.

Secondly, unilateral and single renal cysts are relatively harmless and often neglected clinically. It can occur at any age, but more than 2 / 3 of them are seen in people over 60 years old, which is considered as senile disease. The cyst wall is thin, and it is a single layer of flat epithelium. The cyst contains clear serous fluid, which is produced from the renal parenchyma and protrudes from the surface of renal cortex. The appearance is blue, but it can also be located in the deep layer of renal cortex or medulla.
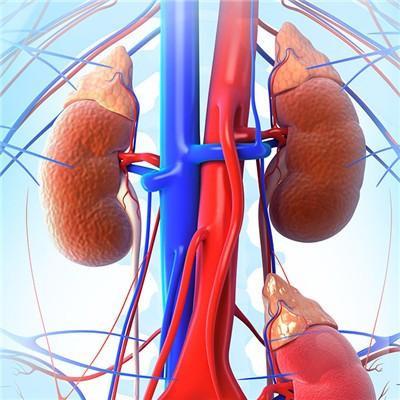
Finally: if the cyst contains clear serous fluid, the wall of the cyst is thick but not smooth, and the fluid is bloody, it indicates that there is possibility of malignant transformation, and the malignant transformation rate is 3% - 7%. Large renal cysts located in the lower pole can compress the ureter, causing obstruction, effusion and infection. The cause of the disease is not completely clear, which may be related to congenital glomerular and tubular structural abnormalities and acquired injury and infection.

matters needing attention
This disease belongs to the category of TCM syndrome. Most of them are visceral cystic diseases caused by Congenital heredity or acquired dystrophy, kidney qi damage and disharmony of collaterals.