Scleroderma symptoms
summary
Scleroderma is a chronic multisystem disease. Initial symptoms are often nonspecific, including Raynaud's phenomenon, fatigue, and musculoskeletal pain. These symptoms last for several weeks or months before other indications appear. The specific early clinical manifestation of scleroderma is swelling and thickening of the skin, which begins in the fingers and hands. Then there are a variety of manifestations, mainly in the skin, lung, heart, digestive tract or kidney. In patients without Raynaud's phenomenon, the risk of renal involvement is increased. Tell us about the symptoms of scleroderma
Scleroderma symptoms
When the patient is cold or nervous, his hands and feet suddenly get cold, the color of his fingers (toes) turns pale, and then turns purple. 10-15 minutes after the end of external stimulation, vasospasm recovered, and the color of finger (toe) end became normal, showing red or mottle. This change is called paroxysmal vasospasm (Raynaud phenomenon). Cold induced pallor can also appear at the tip of nose, tongue, lip and earlobe.
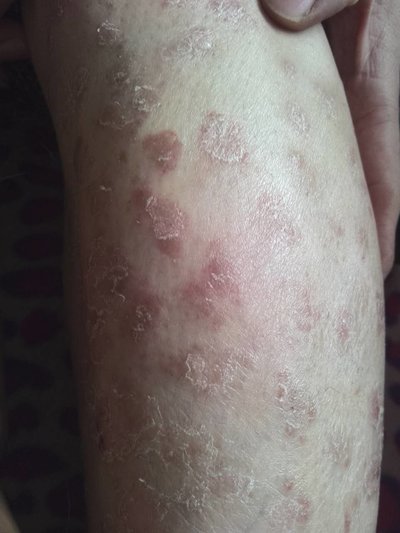
In the early stage of the disease (edema stage), the skin shows mild redness and swelling. Some patients have erythema, pruritus and edema. The early stage of finger edema lasts for a long time. The skin changes stop at the distal end of the upper limb, and can also spread to the forearm, chest, abdomen, back and face. In diffuse scleroderma, the skin hardens extensively with deepening or decreasing pigmentation, making the skin look like salt and pepper.
With the progress of the disease, the skin is tight and shiny, the normal wrinkles and skin folds disappear, and the facial skin is thin, rigid and expressionless. The lips are thin and tight, mouth opening is limited, systemic melanin appears at the same time, some cases even earlier. Patchy telangiectasia and subcutaneous calcification can occur in fingers, face, lips, tongue and forearm. Finger tip is the most common, ranging from small spots to large masses, covering the knee, elbow or other most prominent parts. Calcinosis and telangiectasia are more obvious in patients with CREST syndrome.
matters needing attention
① Remove the infection focus, pay attention to health, strengthen physical exercise, improve the autoimmune function. ② Regular life, work and rest, happy mood, avoid strong mental stimulation. ③ Strengthen nutrition, fasting cold, pay attention to warm supplement.