What symptom does enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli have?
summary
EHEC is a subtype of E.coli. EHEC can be divided into serotypes O157, O26 and o111 according to O antigen. The main pathogenic strain is O157: H7, which can cause infectious diarrhea. E.coli is a normal flora in human and animal intestines and is generally harmless to human. It has three kinds of antigenic structure, namely cell antigen (also known as O antigen), envelope antigen (also known as K antigen) and flagella antigen (also known as H antigen). What symptom does enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli have? Let's talk about it
What symptom does enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli have?
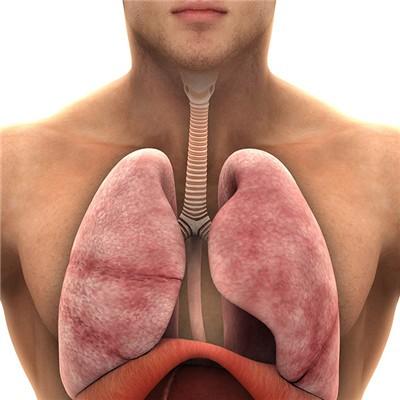
Hemorrhagic enteritis is more common in EHEC infection. The typical manifestations are severe pain and diarrhea in the right lower abdomen, watery stool in the early stage, and then bloody stool or bloody stool similar to lower gastrointestinal bleeding, with medium volume. It is often accompanied by low fever or no fever. The course of disease was 7-10 days, sometimes 12 days. Some patients developed hemolytic uremic syndrome one week after infection.
Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) is a multifactorial disease caused by a series of different etiologies and pathological mechanisms. In addition to enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli, many bacteria and viruses can cause renal hemolytic uremic syndrome, such as Shigella dysenteriae, Salmonella typhi, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Rickettsia like microorganisms, Epstein Barr virus, Coxsackie virus, etc.
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura is similar to renal hemolytic uremic syndrome in clinical characteristics, but nervous system symptoms and fever are more obvious. The disease developed rapidly, and 70% of the patients died within 90 days. Most patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura have five symptoms: fever, thrombocytopenia, microangiopathy hemolytic anemia, renal dysfunction (hematuria, proteinuria, acute renal failure) and neurological symptoms (headache, paresis, coma, intermittent delirium).
matters needing attention
Most outbreaks of EHEC are caused by contamination of food and water. Therefore, it is necessary to strengthen the management of livestock, poultry, meat products and milk. Control measures should be taken from every link of the food chain, that is, the production activities of agriculture and animal husbandry, the processing of non-staple food and the preparation process under factory and family conditions. The key point is to strengthen the management of frozen food, prevent food from being polluted, and develop good living habits. Food should be fully heated before eating, wash hands before and after eating, avoid eating raw vegetables and fruits before eating.