What are the symptoms of Trichomonas vaginalis? Guard against vaginal stench?
summary
Trichomonas is a kind of tiny flagellated protozoa, which can not be seen with naked eyes and must be observed under a microscope. It is generally infected by sexual behavior. Trichomonas vaginalis is a venereal disease caused by Trichomonas (leucorrhea), which occurs in the age group of 35 to 50. Let's share the knowledge about what symptoms of Trichomonas vaginalis are.
What are the symptoms of Trichomonas vaginalis? Guard against vaginal stench?
First: after infected with Trichomonas, the vagina will produce yellowish green foams or rice bran like odorous secretions (commonly known as leucorrhea). Sometimes there will be genital itching or mild pain in the lower abdomen, which can cause vaginal mucosal swelling, redness, congestion and vaginal itch.
Second: a small number of male patients may have urethral secretions, occasionally slight itching, waist pain and other symptoms, but most of the male patients infected with Trichomonas have no obvious symptoms, so men often become the carriers of vaginal Trichomonas.
Third: trichomonal vaginitis is a common vaginitis caused by Trichomonas vaginalis. Trichomonas is pear shaped with a sharp end, about 2-3 times the size of multinucleated leukocytes. There are 4 flagella at the top of the body, undulatory membrane at the body and axon protruding at the back. The living Trichomonas is transparent, colorless and water drop like. The flagella oscillate with the fluctuation of the undulatory membrane. The life cycle of Trichomonas is simple. There is only trophozoite but no cyst stage. The trophozoite has strong vitality and can survive for 2 days at 3-5 ℃; 20-60 minutes at 46 ℃; about 10 hours in semi dry environment; and 45-120 minutes in common soapy water. The vaginal pH value of trichomonas vaginitis patients is generally 5.1-5.4. Trichomonas, hidden in glands and vaginal folds, can reproduce before and after menstruation, causing inflammation.
matters needing attention
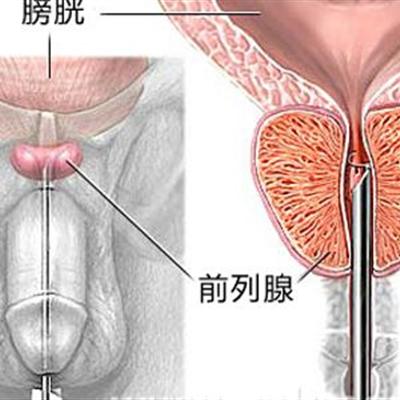
It can consume or phagocytize glycogen in vaginal epithelial cells and block the production of lactic acid. Trichomonas is not only parasitic in vagina. It often invades urethra or paraurethral gland, even bladder, renal pelvis and male prepuce fold, urethra or prostate. It should be checked in hospital in time. The ways of infection are: direct infection: through sexual intercourse; indirect infection: through public baths, bathtubs, baths, swimming pools, toilets, clothing, equipment and dressings.