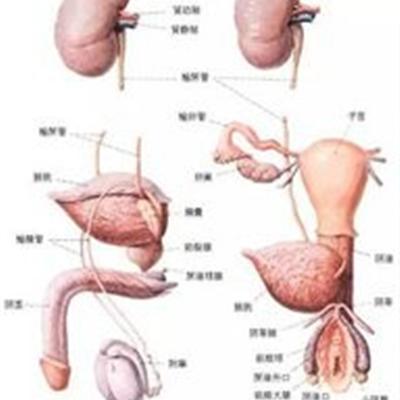
Got prostate hypertrophy how to treat
summary
Excessive sexual life, sexual impulse can significantly increase the congestion of the sexual organs, time for a long time, the prostate will also increase due to persistent congestion. Eating spicy, acid and other food, drinking and other bad habits can also induce prostatic congestion and hyperplasia. Many people are not cured for a long time, not because they can't be cured, but because they don't understand it. Here's how to treat prostatic hypertrophy.
Got prostate hypertrophy how to treat
Treatment 1: laser therapy, laser has coagulation, coking and gasification effect on soft tissue. This method uses the high energy density of laser, which can make the temperature reach 400 ℃ - 1000 ℃ instantly, to burn and vaporize the local tissue rapidly. This method is easy to operate, no bleeding, less postoperative complications and definite curative effect. Now it has been widely used in clinic.
Treatment 2: injection therapy, the application of sclerosing agent directly injected into the prostate through perineum, so that the prostate tissue aseptic necrosis, so that the gland shrinks, improve the patient's urination symptoms. The main side effects were swelling of the prostate after injection, severe pain, and * complications such as urinary retention or cystitis and urethritis. Injection of sclerosing agent can also cause adhesion between prostate and surrounding tissues, which brings difficulties to future surgery.
Treatment 3: cryotherapy. Cryotherapy is to produce deep hypothermia (- 160 ℃ ~ - 180 ℃) in the local area of the prostate to dehydrate the prostate tissue, cause local small vasospasm, blood flow stagnation and thrombosis, thus causing tissue ischemia, hypoxia, necrosis and abscission. This therapy is simple, safe and reliable, and can be used for patients who cannot tolerate open surgery.
matters needing attention
Warm reminder: the purpose of surgical treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia is to relieve urinary tract obstruction and restore normal urination function. There are many different manifestations of bladder dysfunction caused by obstruction. Therefore, comprehensive examination, including urodynamic examination, should be carried out before determining the indications of operation. The condition should be carefully analyzed to understand the relationship between the degree of glandular hyperplasia and obstruction and clinical manifestations, and predict whether the postoperative symptoms will improve, so as to avoid unnecessary operation in inappropriate cases. Urodynamic studies are also needed to identify the cause of postoperative dysuria, chronic urinary retention or incontinence *.