Postpartum infection symptoms?
summary
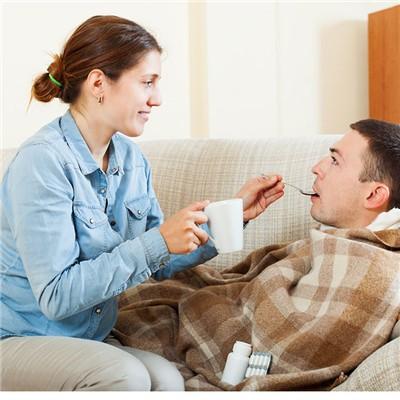
Puerperal infection is a kind of disease that many postpartum women do not want to suffer from. The reason is that it is a disease that has a serious impact on postpartum women's physical recovery, which requires women to know what the symptoms of puerperal infection are, so as to do a good job in prevention. Here are the symptoms of postpartum women's puerperal infection.
Postpartum infection symptoms?
Acute vulvae, vagina, cervicitis: infection caused by perineal injury or operation during delivery, manifested as local burning, pain, falling, purulent secretion stimulation, urethral orifice pain, frequent urination. The wound was infected, the suture was trapped in the swelling tissue, and the pinhole was purulent. Vaginal and cervical infection is characterized by mucosal congestion, ulcers, increased purulent secretions, and later leads to vaginal adhesion or even atresia. If spread to the deep, it can spread to the parauterine tissue, causing pelvic connective tissue inflammation.
Acute endometritis, uterine myositis: pathogens through the placenta exfoliative surface invasion, spread to the decidua, known as endometritis. The infection invades the myometrium, which is called myositis. Endometritis is accompanied by myositis. Severe patients have chills, high fever, headache, fast heart rate, increased white blood cells, lower abdominal tenderness, lochia is not necessarily more and easy to be misdiagnosed.
Acute pelvic connective tissue inflammation, acute salpingitis: pathogens along the para uterine lymph or blood line to the para uterine tissue, there is an acute inflammatory reaction and the formation of inflammatory mass, at the same time affect the mesosalpinx, tube wall. If it invades the whole pelvis, it can also form "frozen pelvis". Gonococcus gonorrhoeae along the genital tract mucosa upward infection, up to the fallopian tube and pelvic cavity, after the formation of abscess, high fever can not retreat.
matters needing attention
At the time of labor, we should eat and drink as much as possible, seize the time to rest, avoid overwork, so as not to reduce the body resistance. If the premature rupture of membranes is too long, or the labor process is too long, or because of residual placental membranes, curettage should be performed, antibiotics should be used to prevent infection.