Symptoms of HIV infection
summary
It is no stranger to mention HIV. HIV is human immunodeficiency virus. It is a retrovirus with strong ability of rapid mutation. This feature not only makes the human immune system difficult to resist its invasion, but also brings difficulties to the development of specific therapeutic drugs and preventive vaccines. HIV directly invades human immune system and destroys cellular and humoral immunity. What are the symptoms of HIV infection.
Symptoms of HIV infection
After the human body is infected with HIV, most people directly enter the latent period of AIDS without any symptoms (generally up to 10 years or so), but some people will have acute symptoms, such as: general discomfort, myalgia, fever, sweating, anorexia, and some people may also have headache, fear of light and virtual meningitis.

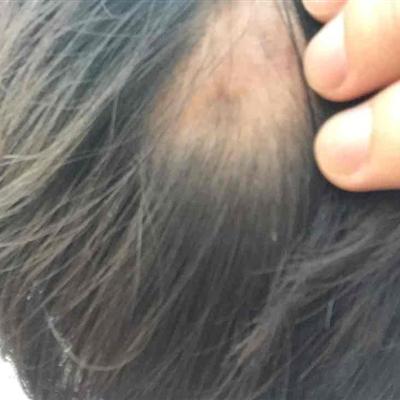
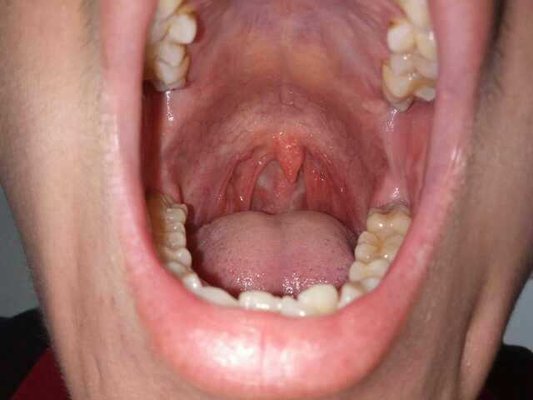
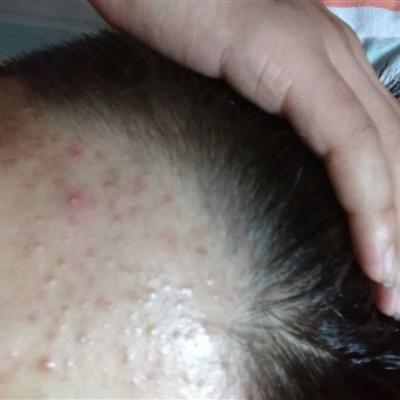
There are about a quarter of patients will also appear rash, often manifested as macular rash or urticaria, appear in the neck, axillary lymph nodes may have swelling, in addition, there are patients with liver, spleen swelling, oral, esophageal mucosal ulcer. A few patients may have neurological symptoms of aseptic meningitis.

It can also cause skin and mucous membrane damage, diffuse papules, herpes zoster, oral and pharyngeal mucositis and ulceration. There may also be a variety of malignant tumors, Kaposi's sarcoma located on the surface of the body can be seen red or purple red spots, papules and invasive masses.

matters needing attention
The initial symptoms of AIDS generally have no specificity. The above symptoms may also be caused by other viruses that lead to the decline of immune function, or may be caused by psychological factors. Therefore, the diagnosis can not be made only based on the symptoms. If you do have high-risk behavior, should be early for HIV antibody testing.