Symptoms of nose fracture
summary
Nasal bone fracture is sometimes single, sometimes combined with jaw fracture. When a person's face is violently impacted by the outside world, or falls suddenly, or is injured by a bullet, it may lead to nose fracture. After the fracture of the nasal bone, there are some lacerations, sometimes directly leading to the fracture of the bridge of the nose. When the fracture occurs, the patient's cartilage can appear dislocation and bending phenomenon, this time the nasal mucosa will be torn, the patient's nasal septum will have perforation. In fact, people's nasal bone is very fragile, very vulnerable to the impact of external forces and fracture. Tell us about the symptoms of nose fracture.
Symptoms of nose fracture
The most common symptom after nasal bone fracture is local pain, many patients will have epistaxis. After fracture, there will be collapse in the upper part of the body or congestion under the skin. And once the nasal bone fracture occurs, the nasal bone will deflect due to the impact of external force.
A few hours after the fracture of the bridge of the nose, the patient's nasal soft tissue will obviously swell. At this time, if you gently pinch the nose, you can have emphysema. Touching the fracture site can cause twisting and obvious pain. If there is secondary infection in nasal bone fracture, it may lead to abscess.
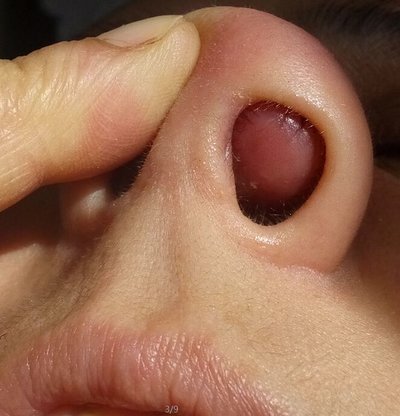
The common phenomenon after nasal bone fracture is nasal bone displacement or acute fracture. Especially after the impact of some major external forces, the displacement or deformity is more obvious. One side of the bridge of the nose will seriously deviate towards the interior of the nasal cavity, and sometimes there may be bilateral deviation at the same time.
matters needing attention
Nasal bone fracture can cause respiratory disorders, because after the fracture, the bone will be displaced to the inner wall of the nasal cavity due to the fracture. At this time, the nasal mucosa will be torn, and some blood clots will form in the nasal cavity, thus blocking the nasal cavity and causing dyspnea.